10 OCT 2023
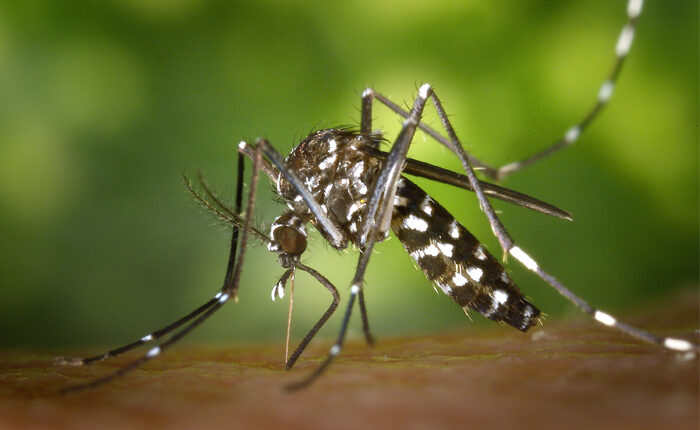
CEPI to invest up to $25.9 million in trials in East Africa to assess a vaccine candidate against Rift Valley Fever (RVF) in people most at risk of infection
The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) is expanding its partnership with Wageningen Bioveterinary Research (WBVR) to advance WBVR’s vaccine candidate against Rift Valley fever (RVF) through a multi-site Phase I/IIa clinical trial. Subject to regulatory and ethical approvals, the anticipated trials are scheduled to begin in 2025 in Kenya and Uganda, two countries where the mosquito-borne disease poses a significant threat to the lives and livelihoods of people in rural communities. Backed with up to US$25.9 million in funding from CEPI, with support from the European Union’s Horizon Europe programme, the studies will be the first to assess the safety and immunogenicity of WBVR’s RVF vaccine in countries where RVF is endemic.
WBVR’s live-attenuated vaccine known as hRVFV-4s, and being further developed under Wageningen spin-off Bunyavax, is currently being evaluated in a Phase I clinical trial in Belgium under a previous CEPI/ EU grant. In addition to the anticipated trials in Kenya and Uganda, CEPI will fund an extension of the ongoing Phase I study to assess immunogenicity up to 24 months; manufacturing of clinical trial materials; epidemiological research to assess the burden of infection and the risk of ‘spillover’ transmission from animals to humans in Kenya and Uganda; and regulatory engagement, including a strategy for achieving licensure of the vaccine. The work will be a combined effort of WBVR with consortium partners Batavia Biosciences BV, Bunyavax BV, CR2O BV, University of Veterinary Medicine Hannover, and Integrum Scientific, LLC.
The official CEPI and WBVR Press Release can be found here.